keos_project2/loader/elf.rs
1//! Utility to parsing ELF file.
2//!
3//! The Executable and Linkable Format (ELF, formerly named
4//! Extensible Linking Format) is a common standard file format for executable
5//! files, object code, shared libraries, and core dumps.
6//!
7//! 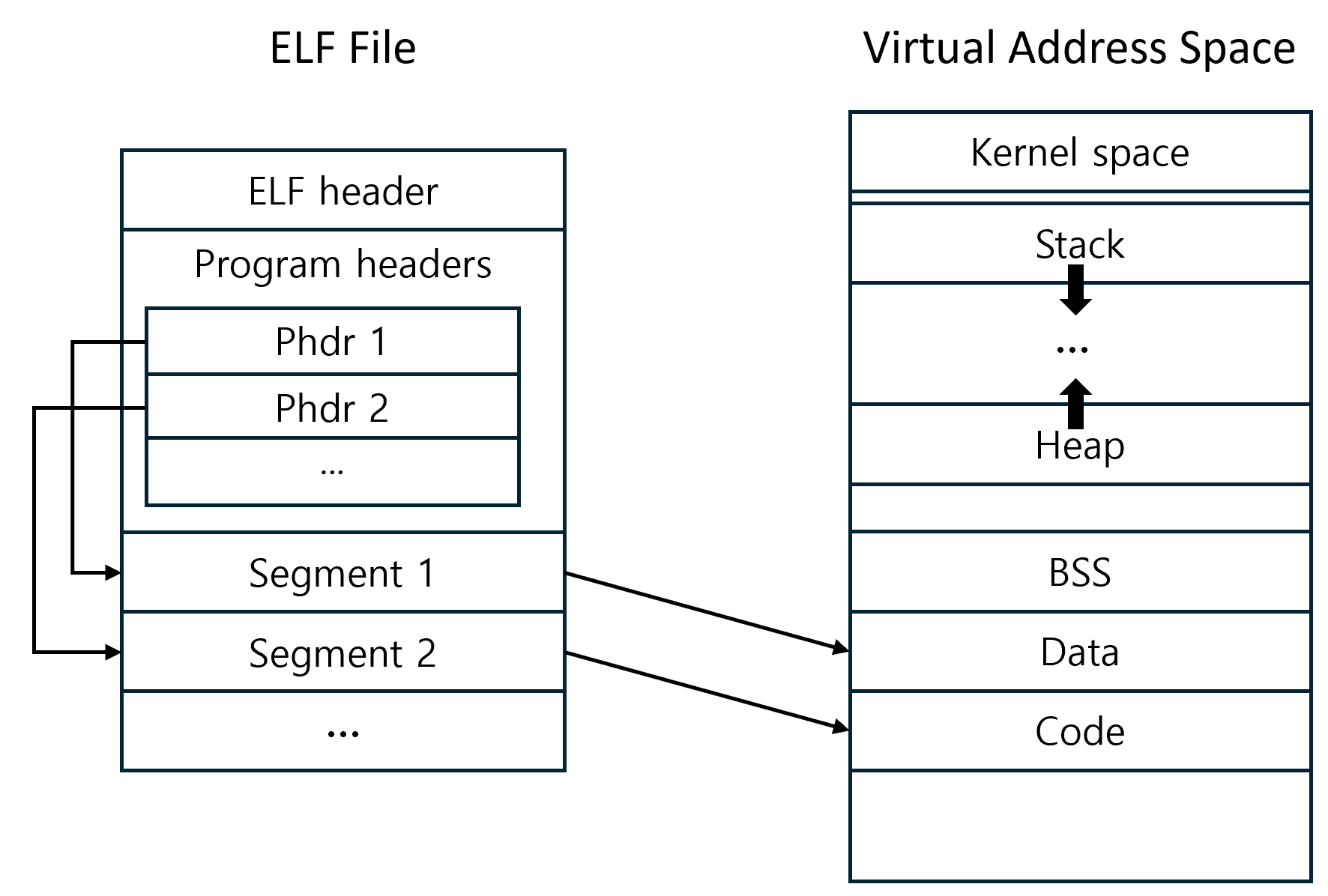
8//! An ELF file has the program header, and section headers. The program headers
9//! show the segments used at run time, whereas the section header lists the
10//! set of sections.
11use alloc::vec::Vec;
12use core::convert::TryInto;
13use keos::{KernelError, fs::RegularFile, mm::page_table::Permission};
14
15/// Represents the ELF file header.
16///
17/// This structure contains metadata about the ELF file, such as its type,
18/// architecture, entry point, and various offsets for program and section
19/// headers.
20#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
21#[repr(C)]
22pub struct ELFHeader {
23 /// The ELF magic number (`0x7F` followed by `ELF` in ASCII).
24 pub magic: [u8; 4],
25 /// Indicates 32-bit or 64-bit format.
26 pub class: u8,
27 /// Specifies little-endian or big-endian encoding.
28 pub data: u8,
29 /// ELF version (set to `1` for the original and current version).
30 pub version: u8,
31 /// Identifies the target operating system ABI.
32 pub abi: u8,
33 /// Further specifies the ABI version.
34 pub abi_version: u8,
35 /// Unused padding bytes (must be zero).
36 pub pad: [u8; 7],
37 /// Object file type (e.g., executable, shared object, relocatable).
38 pub e_type: u16,
39 /// Target instruction set architecture.
40 pub e_machine: u16,
41 /// ELF version (should be `1`).
42 pub e_version: u32,
43 /// Memory address of the entry point where execution starts.
44 pub e_entry: u64,
45 /// Offset of the program header table in bytes.
46 pub e_phoff: u64,
47 /// Offset of the section header table in bytes.
48 pub e_shoff: u64,
49 /// Processor-specific flags.
50 pub e_flags: u32,
51 /// Size of this header in bytes.
52 pub e_ehsize: u16,
53 /// Size of a program header table entry in bytes.
54 pub e_phentsize: u16,
55 /// Number of entries in the program header table.
56 pub e_phnum: u16,
57 /// Size of a section header table entry in bytes.
58 pub e_shentsize: u16,
59 /// Number of entries in the section header table.
60 pub e_shnum: u16,
61 /// Index of the section header table entry that contains section names.
62 pub e_shstrndx: u16,
63}
64
65/// Represents an ELF file in memory.
66///
67/// This struct provides access to ELF metadata and program headers.
68pub struct Elf<'a> {
69 /// A parsed ELF header
70 pub header: ELFHeader,
71 /// Reference to the backing file containing ELF data.
72 pub file: &'a RegularFile,
73}
74
75impl<'a, 'b> Elf<'a> {
76 /// Attempts to create an [`Elf`] object from a [`RegularFile`].
77 ///
78 /// Returns `Some(Elf)` if the file is a valid ELF binary, otherwise `None`.
79 ///
80 /// # Validity Checks
81 /// - Must have the correct ELF magic bytes (`0x7F ELF`).
82 /// - Must be little-endian (`Endian::Little`).
83 /// - Must be 64-bit (`Bit::Bit64`).
84 /// - Must target the x86-64 architecture (`EMachine::Amd64`).
85 pub fn from_file(file: &'a RegularFile) -> Option<Self> {
86 union HeaderUnion {
87 _raw: [u8; 4096],
88 header: ELFHeader,
89 }
90 let header = unsafe {
91 let mut _u = HeaderUnion { _raw: [0; 4096] };
92 file.read(0, &mut _u._raw).ok()?;
93 _u.header
94 };
95
96 if &header.magic == b"\x7FELF"
97 && /* Little Endian */ header.data == 1
98 && /* Bit64 */ header.class == 2
99 && /* Amd64 */ header.e_machine == 0x3E
100 && /* Executable file. */ header.e_type == 2
101 {
102 Some(Self { header, file })
103 } else {
104 None
105 }
106 }
107
108 /// Returns an iterator over the program headers.
109 pub fn phdrs(&'b self) -> Result<PhdrIterator<'a, 'b>, KernelError> {
110 let (base, size) = (self.header.e_phoff.try_into().unwrap(), self.header.e_phnum);
111 let mut buffer = alloc::vec![0; size as usize * 0x38];
112 self.file.read(base, buffer.as_mut())?;
113 Ok(PhdrIterator {
114 cursor: 0,
115 buffer,
116 elf: self,
117 })
118 }
119}
120
121/// Iterator over program headers in an ELF binary.
122///
123/// This iterator is created using [`Elf::phdrs`].
124pub struct PhdrIterator<'a, 'b> {
125 cursor: u16,
126 elf: &'a Elf<'b>,
127 buffer: Vec<u8>,
128}
129
130impl<'a, 'b> core::iter::Iterator for PhdrIterator<'a, 'b> {
131 type Item = Phdr;
132 fn next(&mut self) -> Option<Self::Item> {
133 union Reader {
134 phdr: Phdr,
135 _raw: [u8; 0x38],
136 }
137
138 if self.cursor as usize * 0x38 < self.buffer.len() {
139 unsafe {
140 let ofs = self.cursor as usize * 0x38;
141 let mut inner = Reader { _raw: [0; 0x38] };
142 inner._raw.copy_from_slice(&self.buffer[ofs..ofs + 0x38]);
143 self.cursor += 1;
144 Some(inner.phdr)
145 }
146 } else {
147 None
148 }
149 }
150}
151
152/// ELF program header type.
153///
154/// This enum represents different segment types in an ELF binary.
155#[repr(u32)]
156#[derive(Clone, Copy, PartialEq, Eq, Debug)]
157#[allow(dead_code)]
158pub enum PType {
159 /// Unused segment.
160 Null = 0x0,
161 /// Loadable segment.
162 Load = 0x1,
163 /// Dynamic linking information.
164 Dynamic = 0x2,
165 /// Interpreter path (for dynamically linked executables).
166 Interp = 0x3,
167 /// Auxiliary information.
168 Note = 0x4,
169 /// Reserved.
170 Shlib = 0x5,
171 /// Program header table itself.
172 Phdr = 0x6,
173 /// Thread-Local Storage (TLS) template.
174 Tls = 0x7,
175 /// GNU-specific: Exception handling information.
176 GnuEhFrame = 0x6474e550,
177 /// GNU-specific: Stack segment flags.
178 GnuStack = 0x6474e551,
179 /// GNU-specific: Read-only after relocation.
180 GnuRelro = 0x6474e552,
181 /// GNU-specific.
182 GnuProperty = 0x6474e553,
183}
184
185bitflags::bitflags! {
186 /// Segment permission flags for ELF program headers.
187 ///
188 /// These flags specify whether a segment is readable, writable, or executable.
189 pub struct PFlags: u32 {
190 /// Segment is readable.
191 const READ = 1 << 2;
192 /// Segment is writable.
193 const WRITE = 1 << 1;
194 /// Segment is executable.
195 const EXECUTABLE = 1 << 0;
196 }
197}
198
199#[repr(C)]
200#[derive(Clone, Copy, Debug)]
201/// ELF program header for 64-bit binaries.
202///
203/// Each `Phdr` entry describes a segment or other information needed for
204/// execution.
205pub struct Phdr {
206 /// Segment type.
207 pub type_: PType,
208 /// Segment permissions.
209 pub p_flags: PFlags,
210 /// Offset in the file where the segment starts.
211 pub p_offset: u64,
212 /// Virtual address where the segment should be mapped in memory.
213 pub p_vaddr: u64,
214 /// Physical address (not commonly used in modern OSes).
215 pub p_paddr: u64,
216 /// Size of the segment in the file.
217 pub p_filesz: u64,
218 /// Size of the segment in memory.
219 pub p_memsz: u64,
220 /// Alignment of the segment (must be a power of two).
221 pub p_align: u64,
222}
223
224impl Phdr {
225 /// Get a ELF segment permissions ([`PFlags`]) of this Phdr in forms of
226 /// memory permissions ([`Permission`]).
227 ///
228 /// This function translates the permission flags of phdr into the
229 /// corresponding memory protection flags used by the system and return it.
230 /// The conversion ensures that the memory is properly set up according
231 /// to the ELF segment's requirements.
232 ///
233 /// # Returns
234 /// - A `Permission` value representing the phdr's memory permissions.
235 pub fn permission(&self) -> Permission {
236 let mut permission = Permission::USER;
237 todo!()
238 }
239}